ECG Directory
Welcome to this interactive ECG course.
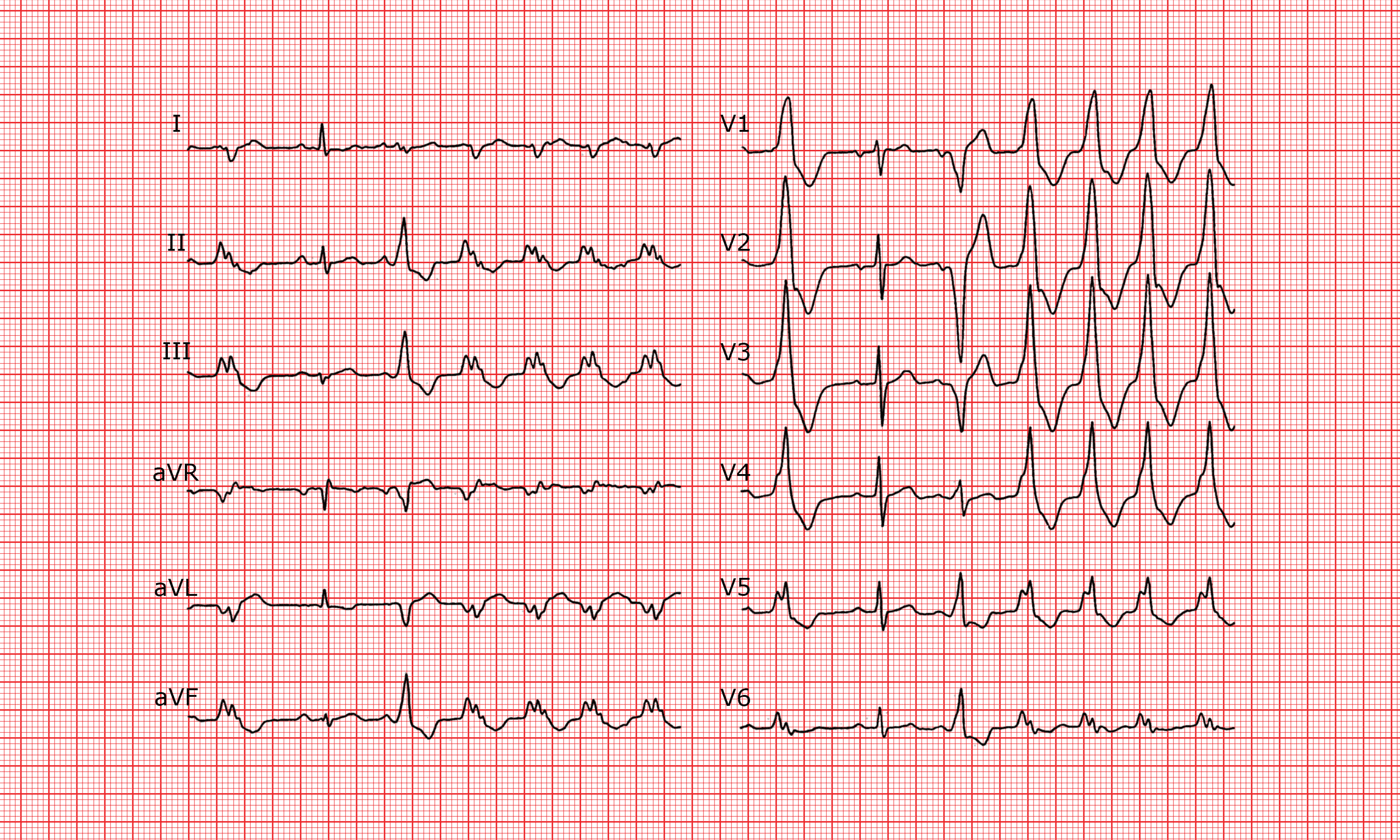
Although it is one of the oldest paraclinic exams, dating back to the late 19th century, the ECG is still of crucial clinical use. This examination often still poses problems of interpretation to the medical practitioner.
This course aims to help the student, the practicing physician and even the trained cardiologist to improve his knowledge in electrocardiography. It consists of 250 traces of varying complexity with a description of each one by experts. This allows the reader to compare his analysis with that of the experts. In addition, the areas of interest of the ECG can be activated to be clearly highlighted.
We hope that these plots will be useful to readers and will improve their knowledge.
The ECGs are available sorted by keywords and categories.